Research Testbeds
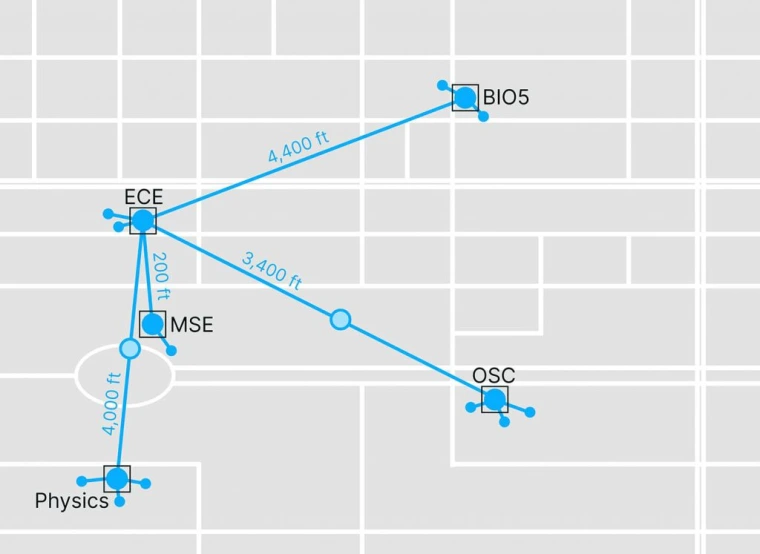
Tucson Testbed
The Tucson’s based Quantum Network System Testbed will be hosted at the University of Arizona and provides a place to test silicon photonic chips with various integrated functionalities, demonstrate entanglement distribution with ever-increasing levels of performance as the program progresses, and test out resource allocation and management protocols developed in the project.
The testbed leverages an existing entangled photon distribution network connected by fiber deployed between five buildings on campus: Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE), Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Physics, Optical Sciences Center (OSC), and Biology (BIO5). With the repeaters developed in the Boston testbed, the Tucson network is building the world’s first quantum network testbed for multi-user 10+M qubits/s fault-tolerant entanglement distribution.

Maryland Testbed
The CQN Maryland Testbed is hosted at the College Park Campus of the University of Maryland and provides a place to integrate trapped-ion quantum processors, diamond color center quantum memory, quantum frequency conversion, and highly-multiplexed entanglement photon source. The testbed aims to demonstrate entanglement distribution with ever-increasing levels of performance as the program progresses, and test out resource allocation and management protocols developed in the project.
The testbed is deployed on the scientific-grade fiber network between four buildings on campus: Kim Engineering Building (KEB), Atlantic Building (ATL), Physical Sciences Complex (PSC), and Institute for Research in Electronics & Applied Physics (IREAP). The 5th building is under construction and will be connected to KEB. By merging novel techniques developed by the Boston testbed team and other collaborators, the Maryland testbed is building the world’s first quantum network testbed for highly-multiplexed heterogeneous entanglement distribution and error correction.
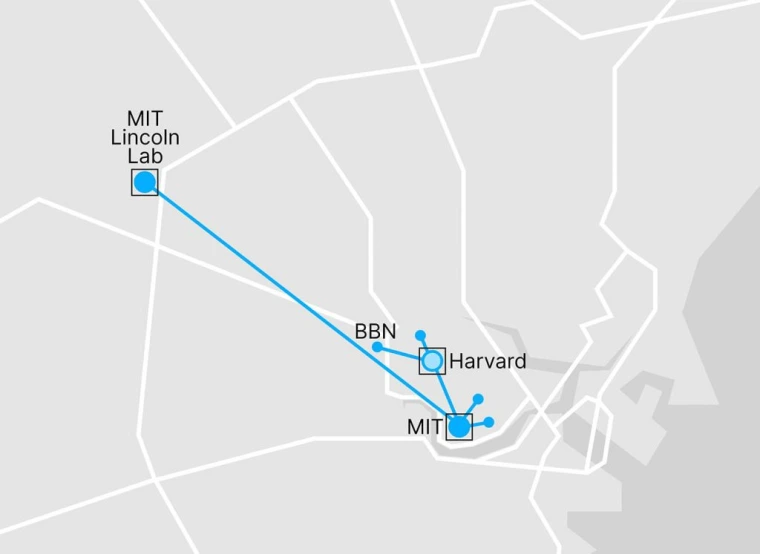
Boston Testbed
The Boston testbed will primarily be focused on building a quantum repeater system developed in Thrust 1, Thrust 2, and Thrust 3. This system will be based on fault-tolerant quantum memories in repeater and switching configurations with the target of achieving high fidelity high rate of entanglement distribution.
The network will consist of repeaters and 42km of fiber from MIT and Lincoln Laboratories. This network will demonstrate the effectiveness of the repeaters by demonstrating a 1Mbit/sec quantum key distribution experiment. The repeaters developed in the Boston Testbed will then be sent to the Tucson testbed to demonstrate a larger, higher bandwidth quantum network.
